Ch3: Basic SQL Query Language
一. Setting up the Database
1. SQL Datatype
CHARACTER(n), CHAR(n): fixed-length character strings
CHARACTER VARYING(n), CHAR VARYING(n):variable-length character strings
NUMERIC(p, s), DECIMAL(p, s), DEC(p, s):
Precision: total number of digits
Scale:number of digits to the right of the decimal point
INTEGER, INT, SMALLINT
FLOAT(p)
REAL
DOUBLE PRECISION
2.Oracle Datatype
Character Datatype
CHAR(n):fixed-length character strings(1 n $\leq$2000)
VARCHAR(n):variable-length character strings(1 n 4000)
LONG:variable-length character data(text data) (maximum size 2GB)
NUMBER Datatype
NUMBER:fixed and floating-point numbers
NUMBER(precision, scale)
NUMBER(*, scale)
Precision:total number of digits
Scale:number of digits to the right of the decimal point(default value is zero)
Negative Scale:rounds the actual data to the specified number of places to the left of the decimal point
3.SQL Statement
1) SQL statements for table creation for CAP database
1 | CREATE TABLE orders ( |
1 | CREATE TABLE orders ( |
1 | -- MYSQL |
2) Select Statement
1 | SELECT * | colname { , colname ... } |
二. Simple Select Statements
1. Relational Algebra与SQL语法对比
1. Query in relational algebra :
(R where Condition) [A, A, …, A]
Query in SQL:
1 | Select A1, A2,...,Am from R where Condition; |
2. Query in relational algebra :
((R R…R) where Condition) [A, A, …, A]
Query in SQL:
1 | Select A1, A2,...,Am from R1, R2,...,Rn where Condition; |
3. Query in relational algebra :
Head® = {A,…,A,B,…,B}, Head(S) = {B,…,B, C,…,C}
((RS) where Condition) [A, A, …, A]
Query in SQL:
1 | Select A1, A2,...,Am from R, S where Condition and R.B1 = S.B1 and R2.B2 = S.B2 and...and R.Bk = S.Bk; |
4. Query in relational algebra :
(R S) [A, A, …, A]
Query in SQL:
1 | Select A1, A2,...,Am from R,S where Condition; |
5. Query in relational algebra :
(AGENTS where city = ‘New York’) [aid, aname]
Query in SQL:
1 | Select aid, aname from agents where city = 'New York'; |
6. Query in relational algebra :
(CUSTOMERS) [cid, cname, city, discnt]
Query in SQL:
1 | Select * from Customers; |
1 | Select cid, cname, city, discnt from Customers; |
7. Query in relational algebra :
((C[cid, cname] O)A) [cname, aname];
((C O A) where C.cid = O.cid and O.aid = A.aid) [cname, aname]
Query in SQL:
1 | Select distinct cname, aname from customers, orders, agents where customers.cid = orders.cid and orders.aid = agents.aid; |
2. Some Examples
1. Display all values of customers in table CUSTOMERS.
1 | SELECT cid, cname, city, discnt FROM customers ; |
1 | SELECT * FROM customers ; |
2. Retrieve all (cname, aname) pairs where the customer places an order through the agent.
1 | SELECT distinct cname, aname |
1 | SELECT distinct cname, aname |
3. Get the names of customers who order at least one product priced at $0.50.
1 | SELECT cname |
4. Retrieve customers who place orders only through agent a03.
O [cid] - (O where aid <> ‘a03’) [cid]
1 | SELECT o1.cid |
5. List all pairs of customer cids based in the same city.
1 | Select c1.cid, c2.cid from customers c1, customers c2 where c1.city = c2.city and c1.cid < c2.cid; |
3. Table and column alias
Table alias in FROM clause
方法1:table_name as alias_name
方法2:table_name alias_name
column alias in SELECT clause
column_name as alias_name
4. ALL | DISTINCT
SELECT aid, pid FROM orders ;
SELECT distinct aid, pid FROM orders ;
Find pids of products ordered by at least two customers.
1 | SELECT distinct pid |
1 | SELECT distinct pid |
三. Subqueries
1. The IN Predicate
1. Retrieve cids of customers who place orders with agents in Duluth or Dallas.
1 | select distinct cid |
1 | select distinct cid |
2. Get all information concerning agents based in Duluth or Dallas.
1 | SELECT * |
3. Get the names and discounts of all customers who place orders through agents in Duluth or Dallas.
1 | SELECT cname, discnt |
4. Find the names of customers who order product p05.
1 | Select distinct cname |
1 | Select distinct cname |
5. Get cids of customers who place an order through at least one agent who places an order for product p03
T1 := (O where pid = ‘p03’) [aid]
T2 := (T1 $\infty $ O) [cid]
1 | select o2.cid from orders o1, orders o2 |
1 | select o2.cid from orders o2 where o2.aid IN |
6. Get cids of all customers who have the same discount as any customer in Dallas or Boston.
T1 := (C where city = ‘Dallas’ or city = ‘Boston’) [discnt]
T2 := (T1 C) [cid]
1 | select c2.cid from customers c1, customers c2 |
1 | select c2.cid from customers c2 where c2.discnt IN |
7. Get pids of products not ordered by any customer living in a city whose name begin with the letter D.
1 | select p.pid from products p where p.pid NOT IN |
注意:IN 操作符允许您在 WHERE 子句中规定多个值。
4. Find ordno values for all orders placed by customers in Duluth through agents in New York.
1 | SELECT ordno |
2. The Quantified Comparison Predicate
expr { SOME | ANY | ALL } ( subquery )
IN is =SOME,=ANY
NOT IN is <>ALL
注意:主要用于某一类属性值的比较;或用于替代IN;或求某一类属性最大/最小时的其他属性的值
1. Find aid values of agents with a minimum percent commission.
1 | SELECT aid |
1 | Select aid |
2. Find all customers who have the same discount as that of any of the customers in Dallas or Boston.
1 | SELECT cid, cname |
3. Get cid values of customers with discnt smaller than those of any customers who live in Duluth.
1 | SELECT cid, cname |
4. Find cid values of customers with discnt smaller than a customer who lives in Duluth.
1 | SELECT cid |
注意:
1) > ALL 父查询中的结果集大于子查询中每一个结果集中的值,则为真
2) > ANY, SOME 父查询中的结果集大于子查询中任意一个结果集中的值,则为真
3) = ANY 与子查询 IN相同
4) <> ANY 与 NOT IN 父查询中的结果集不等于子查询中的a或者b或者c,则为真
3. The EXISTS Predicate
实例:
exists,not exists的使用方法示例,需要的朋友可以参考下。
学生表:
1 | create table t_student |
选课表:
1 | create table select_course |
课程表:
1 | create table COURSE |
1.查询选修了所有课程的学生id、name:(即不存在这样一个学生,他有一门课程没有选。)
分析:
如果有一门课没有选,则此时
(1)select * from select_course sc,t_student ts,course c where sc.student_id=ts.id and sc.course_id=c.id存在null,
这说明(2)select * from course c 的查询结果中确实有记录不存在(1查询中),查询结果返回没有选的课程,
此时select * from t_student ts 后的not exists 判断结果为false,不执行查询。
1 | select id, name from t_student ts where not exists |
1 | select id, name from t_student ts, |
2.查询没有选择所有课程的学生,即没有全选的学生。(存在这样的一个学生,他至少有一门课没有选)
分析:
只要有一个门没有选,即
select * from select_course sc,t_student ts,courses c where student_id=t_student.id and courses_id=courses.id 有一条为空,
即not exists null 为true,此时select * from courses有查询结果(id为子查询中的courses.id ),
因此select id,name from t_student 将执行查询(id为子查询中t_student.id )。
1 | select id,name from t_student where exists |
1 | select id name from t_student where (id ,name) NOT IN |
3.查询一门课也没有选的学生。(不存这样的一个学生,他至少选修一门课程)
分析:
如果他选修了一门select * from course结果集不为空,not exists 判断结果为false;
select id,name from t_student 不执行查询。
1 | select id,name from t_student where not exists |
1 | select id, name from t_student where id NOT IN |
4.查询至少选修了一门课程的学生。(存在这样的一个学生,他至少选修一门课程)
1 | select id,name from t_student where exists |
1 | select id, name from t_student where (id, name) NOT IN |
注意:在插入记录前,需要检查这条记录是否已经存在,只有当记录不存在时才执行插入操作,可以通过使用 EXISTS 条件句防止插入重复记录。
1 | INSERT INTO TableIn (ANAME,ASEX) |
| Relational Algebra | SQL Predicate |
|---|---|
| natural join | IN |
| =SOME | |
| EXISTS | |
| difference | NOT IN |
| <>ALL | |
| NOT EXISTS |
1. Retrieve all customer names where the customer places an order through agent a05.
1 | Select distinct c.cname |
1 | select distinct c.cname |
2. Find all customer names where the customer does not place an order through agent a05.
1 | SELECT cname |
1 | SELECT cname |
3. Find cids of all customers who don’t place any order through agent a03.
1 | SELECT cid |
1 | SELECT cid |
注意:
EXISTS用于检查子查询是否至少会返回一行数据,该子查询实际上并不返回任何数据,而是返回值True或False
not in和not exists的区别:
1. not in 只有当子查询中,select 关键字后的字段有not null约束或者有这种暗示时用not in,另外如果主查询中表大,子查询中的表小但是记录多,则应当使用not in,
例如:查询那些班级中没有学生的:
1 | select * from class where cid not in |
2. 当表中cid存在null值,not in 不对空值进行处理
解决:
1 | select * from class where cid not in |
not in的执行顺序是:是在表中一条记录一条记录的查询(查询每条记录)符合要求的就返回结果集,不符合的就继续查询下一条记录,直到把表中的记录查询完。也就是说为了证明找不到,所以只能查询全部记录才能证明,并没有用到索引。
not exists:如果主查询表中记录少,子查询表中记录多,并有索引。
例如:查询那些班级中没有学生的
1 | select * from class2 |
not exists的执行顺序是:在表中查询,是根据索引查询的,如果存在就返回true,如果不存在就返回false,不会每条记录都去查询。
之所以要多用not exists,而不用not in,也就是not exists查询的效率远远高与not in查询的效率。
4. The LIKE Predicate
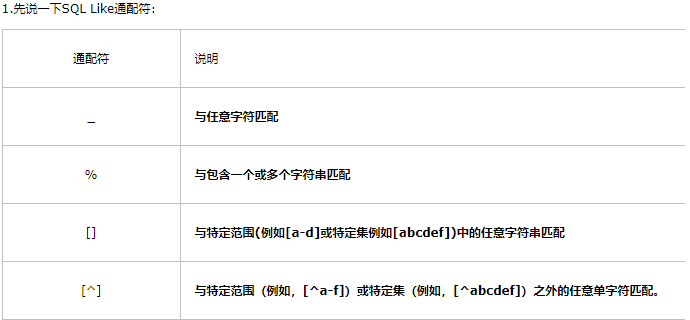
1. Get pids of products not ordered by any customer living in a city whose name begin with the letter D.
1 | SELECT p.pid |
2. Retrieve cid values of customers whose cname does not have a third letter equal to ‘%’.
1 | Select cid |
注意:% 原为通配符,指定用 ’ \ '符号来说明跟在其后面的通配符字符为普通字符。
3. Retrieve cid values of customers whose cname begins “Tip_” and has an arbitrary number of characters following.
1 | Select cid |
4. Retrieve cid values of customers whose cname starts with the sequence “ab\”.
1 | Select * |
( 连续的两个转义指示字符表示 ‘转义指示符 ’自己)
注意:
‘A_Z’: 所有以 ‘A’ 起头,另一个任何值的字原,且以 ‘Z’ 为结尾的字串。
‘ABC%’: 所有以 ‘ABC’ 起头的字串。
‘%XYZ’: 所有以 ‘XYZ’ 结尾的字串。
‘%AN%’: 所有含有 ‘AN’ 这个套式的字串。
使用 ESCAPE 关键字定义转义符。
WHERE ColumnA LIKE ‘%5/%%’ ESCAPE ‘/’ 即 ‘/’为转义字符,第二个‘%’为普通字符,第一、第三个为通配符。
5. The NULL Predicate
NULL表示不可知不确定,NULL不与任何值相等(包括其本身)
IS NULL 判断某个字符是否为空,并不代表空字符或者是0
=NULL 是判断某个值是否等于NULL
总之,要判断一个数是否等于NULL只能用 IS NULL 或者 IS NOT NULL 来判断
1 | -- 选择非空列 |
6.Example of Subqueries
1. Retrieve all customer names where the customer places an order through agent a05.
1 | SELECT distinct cname |
1 | SELECT distinct cname |
1 | SELECT distinct cname |
2. Get cids of customers who order both products p01 and p07.
1 | SELECT o1.cid FROM orders o1, orders o2 |
1 | SELECT o1.cid FROM orders o1 |
1 | Select cid from orders where pid = 'p01' |
3. Get cids of customers who place an order through at least one agent who places an order for product p03.
T1 := (O where pid = ‘p03’)[aid]
T2 := (T1 O) [cid]
1 | SELECT o2.cid |
4. Get cids of all customers who have the same discount as any customer in Dallas or Boston.
1 | SELECT c1.cid |
5. Find all customer names where the customer does not place an order through agent a05.
((C[cid] – (O where aid = ‘a05’) [cid]) C) [cname]
1 | SELECT cname |
1 | SELECT cname |
注意:此处可以看见NOT EXISTS需要将索引联结起来;而NOT IN则不需要
6. Find all cid, aid pairs where the customer does not place an order through the agent.
1 | SELECT cid, aid |
1 | SELECT cid, aid |
注意:此处也可以看见NOT EXISTS需要将索引联结起来;而NOT IN则不需要
7. Get the names of customers who order at least one product priced at $0.50.
1 | SELECT cname |
8. Retrieve customers who place orders only through agent a03
O [cid] - (O where aid <> ‘a03’) [cid]
1 | SELECT o1.cid |
四.UNION Operators and FOR ALL Conditions
1. The UNION Operator(并集/交集拓展)
1. Retrieve all cities where either a customer or an agent, or both, is based.
1 | select city from customers |
1 | select city from customers |
1 | select city from customers |
注意:
如果我们需要将两个或多个select语句的结果作为一个整体显示出来,这是我们就需要用到union或者union all关键字。
union和union all的区别是,union会自动压缩多个结果集合中的重复结果,而union all则将所有的结果全部显示出来,不管是不是重复。
拓展:求交集
1. Get cid values of customers who order both products p01 and p07.
(Orders where pid = ‘p01’) [cid] (Orders where pid = ‘p07’) [cid]
1 | select o1.cid from Orders o1 |
1 | select cid from (select cid from Orders where pid = 'p01') t1, |
2. The Division Operation in Relational Algebra
注意:
1. 可将关系代数中的除法运算转换为SQL语句的NOT EXISTS二重条件判断
2. 写出关系代数式(包含除法运算)根据表关系构造NOT EXISTS二重条件判断
3. NOT EXISTS判断为Select *,且需要建立索引
1. Find cids of customers who place orders with ALL agents based in New York.
o[cid, aid] (a where city=‘New York’)[aid]
1 | SELECT c.cid |

2. Get the aid values of agents in New York or Duluth who place orders for all products costing more than a dollar.
1 | SELECT aid |
3. Find aid values of agents who place orders for product p01 as well as for all products costing more than a dollar.
1 | SELECT aid FROM agents a |
4. Get cids of customers who order all products that anybody orders.
O[cid, pid] ÷ O[pid]
1 | SELECT c.cid FROM customers c |
5. Get aids of agents who take orders on at least that set of products ordered by c004.
O[aid, pid] ÷ (O where cid = ‘c004’)[pid]
1 | SELECT a.aid |
6. Get cids for customers with the following property:
If customer c006 orders a product x through agent y, so the customer orders the product x through the agent y.
1 | SELECT cid |
7. Get aids of agents who place orders for all customers who place orders for all products costing more than a dollar through the agent.
1 | SELECT aid |
注意:
Relational Algebra:
R(x, y) S(y)
Relational Calculus:
z ( y ( P(z, y) )) z ( y ( P(z, y) ))
3. Set Functions in SQL(聚合函数)

1. Get the total dollar amount of all orders.
1 | select sum ( dollars ) as totaldollars |
2. Get the total quantity of product p03 that has been ordered.
1 | select sum ( qty ) as TOTAL |
3. List the cid values of all customers who have a discount less than the maximum discount.
1 | select cid |
4. Find products ordered by at least two customers.
1 | select p.pid |
注意:
1. 此处表示至少有两个顾客购买的产品;
2. 具体语句运行过程:
a. 先将两表连接;
b. 然后返回相等pid下cid不重复的记录数;
c. 若相同pid的该记录数大于2,则返回其pid;
1 | select p.pid from ( |
注意:
1. 先将orders表pid,cid不重复记录分组构造新表t;
2. 再将produsts表与t表连接,最后返回cid不重复记录数大于2的pid;
1 | SELECT pid |
注意:使用Group By对pid进行分组,Having对cid进行过滤
注意:
1. count(*):获取数量
2. sum():求和(这里要注意求和是忽略null值的,null与其他数值相加结果为null,所以可以通过ifnull(xxx,0)将null的值赋为0
3. avg():求平均数
4. max():求最大值
5. min():求最小值
4. Groups of Rows in SQL
GROUP BY clause & HAVING clause
SQL语句的执行顺序:
from–where–group by–having–select–order by
from:需要从哪个数据表检索数据
where:过滤表中数据的条件
group by:如何将上面过滤出的数据分组
having:对上面已经分组的数据进行过滤的条件
select:查看结果集中的哪个列,或列的计算结果
order by:按照什么样的顺序来查看返回的数据
1) GROUP BY
GROUP BY语句用来与聚合函数(aggregate functions such as COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, or MAX.)联合使用来得到一个或多个列的结果集。
因为聚合函数通过作用于一组数据而只返回一个单个值,因此,在SELECT语句中出现的元素要么为一个聚合函数的输入值,要么为GROUP BY语句的参数,否则会出错。
例如,对于上面提到的表格,我们做一个这样的查询:
1 | SELECT id, COUNT(course) as numcourse, score |
此时查询便会出错,错误提示如下:
Column ‘student.score’ is invalid in the select list because it is not contained in either an aggregate function or the GROUP BY clause.
出现以上错误的原因是因为一个学生id对应多个分数,如果我们简单的在
SELECT语句中写上score,则无法判断应该输出哪一个分数。如果想用score作为
select语句的参数可以将它用作一个聚合函数的输入值,如下例,我们可以得到每个
学生所选的课程门数以及每个学生的平均分数:
1 | SELECT id, COUNT(course) as numcourse, AVG(score) as avgscore |
1. Find the agent name and aid, and the product name and pid, together with the total quantity each agent supplies of that product to customers c002 and c003.
1 | SELECT a.aid, a.aname, p.pid, p.pname, sum(qty) |
注意:多表连接也可以使用Group By进行分组
2.对某个字段分组且进行数据统计,可使用count(*)技巧
例如说明现在有一个这样的表:每个部门有多少人 就要用到分组的技术
1 | select DepartmentID as '部门名称', |
这个就是使用了group by +字段进行了分组,其中我们就可以理解为我们按照了部门的名称ID,DepartmentID将数据集进行了分组;然后再进行各个组的统计数据分别有多少;
通俗一点说:group by 字段1,字段2。。。(整个表中不止这两个字段)表示数据集中字段1相等,字段2也相等的数据归为一组,只显示一条数据。那么你可以对字段3进行统计(求和,求平均值等);
3.MySQL中group by的时候字段不加聚合函数的情况
首先对于不加聚合函数的sql语句来说,它的功能结合了limit来得出结果,仔细想想的时候有点Oracle分析函数的味道,limit的时候得到的并不是最大最小的值(元素按照原来在表中的默认顺序结合分组),而是某一下group by结果集中第一行,也就是刚才说的相当于先group by, 然后在每个group by下面进行limit 1。
其次,刚才还说了常规的group by结合聚合函数的时候,选择的字段除了聚合函数外,必须在group by中存在,但是在mysql中不是这样了,它具有隐含字段的功能,例如:
1 | select a,b,c,count(*) from test1 group by a,b; |
| a | b | c | count(*) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
注意:对于没有选择的字段,上面是c,c的值还是和上面说到的一样,是根据得到的结果集然后根据每个group by 进行limit 1得到的结果。
2) HAVING
HAVING语句通常与GROUP BY语句联合使用,用来过滤由GROUP BY语句返回的记录集。
HAVING语句的存在弥补了WHERE关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足(只能接聚合函数进行筛选)。
1. Find all product and agent IDs and the total quantity ordered of the product by the agent, when this quantity exceeds 1000.
1 | SELECT pid, aid, sum(qty) as total |
2. Provide pid values of all products purchased by at least two customers.
1 | SELECT pid |
3. Find the average, over all agents, of the maximum dollar sales made by each agent.
Right:
1 | SELECT avg ( t.x ) |
Wrong:
1 | SELECT avg ( select max ( dollars ) from orders ) |
5. Insert, Update, and Delete Statements
1) The Insert Statement
1 | INSERT INTO tablename [ ( colname, ...... ) ] |
- 带有子查询
1 | INSERT INTO T_ReaderFavorite2 (FCategoryId, FReaderId) |
这里使用SELECT FCategoryId,FReaderId FROM T_ReaderFavorite将T_ReaderFavorite表中的数据读出,然后使用INSERT INTO T_ReaderFavorite2(FCategoryId,FReaderId)将检索结果插入到T_ReaderFavorite2 表中,注意上下的列顺序必须是一一对应的。
1 | INSERT INTO T_ReaderFavorite(FCategoryId,FReaderId) |
SELECT语句从T_Reader表中检索所有的读者信息,并且将第一列设定为固定值1,而将第二列设定为读者的主键,执行完毕查看T_ReaderFavorite表中的内容。
2) The Update Statements
1 | UPDATE tablename |
1. Give all customers who have total orders of more than $1000 a 10% increase in the discnt they receive.
1 | UPDATE customers |
注意:可利用Select不包含聚合函数,Having包含聚合函数进行单一筛选!
1 | UPDATE customers c |
- 多张表UPDATE用法
- 当用一个表中的数据来更新另一个表中的数据,T-SQL提供多种写法(下面列出了二种),但建议用第一种写法,虽然传统,但结构清晰。
并且要注意,当用一个表中的数据来更新另一个表中的数据时,二个表一定要有关联!
1 | update t1 set t1.c2 = t2.c2 |
1 | Update t1 set t1.c2 = t2.c2 |
1 | Update t1 set t1.c2 = t2.c2 |
注意:用using关键字进行简化
1.查询必须是等值连接。
2.等值连接中的列必须具有相同的名称和数据类型。
表联结(join)拓展:
相同多列联结:
1 | select... from table1 inner join table2 |
相当于
1 | select... from table1 inner join table2 |
1 | select... from table1, table2 |
多表联结:
1 | select... from table1 |
相当于
1 | select... from table1,table2,table3 |
1 | select... from table1 |
- FROM 子句中指定的表的别名不能作为 SET column_name 子句中被修改字段的限定符使用。
1 | UPDATE titles |
- 若要使上例合法,请从列名中删除别名 t 或使用本身的表名。
1 | UPDATE titles |
- 更新多列
1 | update mytab a |
1. 多表关联update的时候,记得要加exists()条件,否则不满足条件的记录被update称NULL:
比如:stu表存在,但stu1表不存在的数据,对应的字段会被update成NULL;2. oracle在进行更新时无法join, 所以我们用exists来进行连表条件查询,相当于mytab表和goal表关联,当id相等时才执行更新!
- Update与判断操作的结合
1. if(true,a,b), if(false,a,b) 这个就是第一个如果是true,就等于a,false就等于b,有点像三元表达式
2. case when then else end
(Eg.)性别互换:
1 | update salary set sex = if(sex = 'm','f','m'); |
3) The Delete Statement
1 | DELETE |
多表删除
多表删除是指从一个或多个表中删除满足条件的数据,其中的 table_references代表了多个表的join操作,例如以下两个例子代表
从t 1和t 2表中删除满足条件的数据
1 | DELETE FROM somelog WHERE user = 'jcole' ORDER BY timestamp_column LIMIT 1; |
- 对多表删除语句而言,如果想对表使用别名,则只能在 table_references子句中使用,否则会报错。
1 | DELETE a1, a2 FROM t1 AS a1 INNER JOIN t2 AS a2 ON a1.id=a2.id; -- 正确 |
1. Give all agents in New York a 10% raise in the percent commission they earn on an order.
1 | UPDATE agents |
2. Give all customers who have total orders of more than $1000 a 10% increase in the discnt they receive.
1 | UPDATE customers |
3. Delete all agents in New York.
1 | DELETE FROM agents |
4. Delete all agents who have total orders of less than $600.
1 | DELETE FROM agents |
Ch4.Object-Relational SQL
一. Object Types
1.定义新的数据类型(对象类型)
- 对象类型的创建与删除
1 | CREATE TYPE typename AS OBJECT |
1 | DROP TYPE typename; |
- 创建一个 ’姓名’(name_t) 类型
1 | CREATE TYPE name_t AS OBJECT ( |
2.对象类型的使用方法
- 使用已有的对象类型来创建新的类型或表
1 | CREATE TYPE person_t AS OBJECT ( |
3.使用对象数据类型来直接创建一张表
- CREATE TABLE tablename OF typename
{ ( constraint-define ) } ;
1 | CREATE TABLE people OF person_t (PRIMARY KEY(ssno)) ; |
4.对象值的创建、查询与更新
- 对象值的创建
1 | Insert into teachers values |
- 对象值的查询
1 | Select t.tid, t.name_t.fname, t.name_t.lname |
- 对象值的更新
1) 修改元组中的对象属性值
1 | update people p |
2) 修改某个对象属性值的成员属性
1 | update people p |
3) 修改整个元组
1 | update people p |
5.对象的引用类型
- 对象的引用类型:REF < object type >
是指向某个元组对象的指针类型
可用于实现对象类型之间的嵌套引用
- 在使用含有 REF类型的对象类型(Object Type)来创建关系表时,必须使用Scope for子句来限制REF属性的取值范围。
1) 定义类型之间的引用关系
定义基本的对象类型:
customer_t, agents_t, products_t
1 | create type customer_t as object ( |
1 | create type agent_t as object ( |
1 | create type product_t as object ( |
定义类型之间的引用关系 :
1 | create type order_t as object ( |
(新增三个REF属性,分别引用(指向)三个不同的元组对象(Row Object))
2) 创建含有引用类型的关系表
使用前面定义的对象类型创建基本关系表 :
1 | create table customers of customer_t |
1 | create table products of product_t |
1 | create table agents of agent_t |
创建含有引用类型的关系表
1 | create table orders of order_t ( |
3) 引用关系查询
根据元组之间的REF引用关系进行查询
1 | select o.ordno, o.ordcust.cname |
1. Find pid values of products that have been ordered by at least two customers.
1 | select distinct x1.pid |
ordcust 承担起了 cid 所担负的责任!
1 | select distinct x1.pid |
4) 函数与谓词
- 函数与谓词
1.获取对象(元组)的引用指针: REF(……)
2.返回引用指针所指向对象的值: DEREF(……)
两个谓词
IS DANGLING
用于判断所引用的元组对象是否存在
如果所引用的元组对象不存在,那么该谓词返回逻辑真(TRUE),否则返回逻辑假(FALSE)。
该谓词主要用于检查那些错误的对象引用指针。
IS NULL
1. Retrieve all customer names where the customer does not place an order through agent a05.
1 | select c.cname |
1 | select o.cid from orders o |
等价于:
1 | select o.cid from orders o |
5) 类型的循环嵌套定义
- 对象类型(object type)不能嵌套定义,但 REF 关系可以实现嵌套引用。
1 | create type police_officer_t as object |
- 可以使用对象类型 police_officer_t 来创建表
1 | create table police_officers of police_officer_t |
- 在表 police_officers 上的对象查询的例子
1. Retrieve the last names of all police officers who have partners over sixty years of age.
1 | select p.pol_person.pname.lname |
6) 其它约束
- 有关 REF定义的其它约束 (REF Dependencies)
1) 两张表之间的相互 REF关系的定义
首先,定义两个具有相互REF关系的对象类型 (create type …… )
再用创建好的对象类型创建关系表
2) 两个具有相互REF关系的表/类型的删除
在删除类型(drop type)之前需要先删除表(drop table)
在删除类型(drop type)时需要采用强制删除的方式
1 | DROP TYPE typename FORCE; |
先不管REF属性的赋值(先置为NULL),然后再使用UPDATE操作修改REF属性上的取值
1 | update orders o |
二. Collection Types(集合类型)
1.Table Types ( Nested Tables )
1) 创建一个新的表类型 (table type)
1 | CREATE TYPE dependents_t |
2) 使用类型dependents_t来定义表employees中的属性并形成一个嵌套表(nested table)定义。
1 | create table employees ( |
3) Nested table的访问
table ( … ) 的使用
Oracle 不支持直接对嵌套表属性的统计查询功能,即下述的统计查询操作是错误的:
1
2
3select count(e.dependents)
from employees e
where e.eid = 101;应为:
1
2
3
4Select count(*)
From table (
select e.dependents
from employees e where e.eid = 101);Oracle 数据库没有提供 nested table 的相等比较运算。
可以使用 IN 操作符来实现某些需要通过 nested table 进行的查询功能
Oracle提供了单个对象的相等比较功能
1. Retrieve eids with dependents that have name given by
name_t(‘Lukas’, ‘David’, ‘E’)1
2
3
4select eid from employees e
where name_t(‘Lukas’, ‘David’, ‘E’) in
( select d.pname
from table(e.dependents) d);Nested Cursors (嵌套游标)
(i) 普通的查询操作
1
2
3select e.eid, d.ssno as dep_sso
from employees e, table(e.dependents) d
where d.age < 16;(ii) 使用 nested cursor 的查询操作
1
2
3
4select e.eid, cursor(select d.ssno as dep_ssno
from table(e.dependents) d
where d.age < 16) dep_tab
from employees e;
2.Array Types
1) Array Types for VARRAYs
1. 自定义一个TYPE使用 VARRAY来得到一个数组但只能对基本类型定义。
2. VARRAY数据结构可存储相同类型元素的一个固定大小的连续集合。
3. VARRAY用于存储数据的有序集合,但它往往是更加有用认为数组作为相同类型的变量的集合。
- 一个VARRAY类型是用CREATE TYPE语句创建。必须指定最大长度,并存储在 VARRAY元素的类型。
PL/SQL 块创建 VRRAY类型的基本语法:
1 | TYPE varray_type_name IS VARRAY(n) of <element_type> |
create type extensions_t as varray(4) of int;
使用 Array Types 定义表中的属性
1 | create table phonebook ( |

